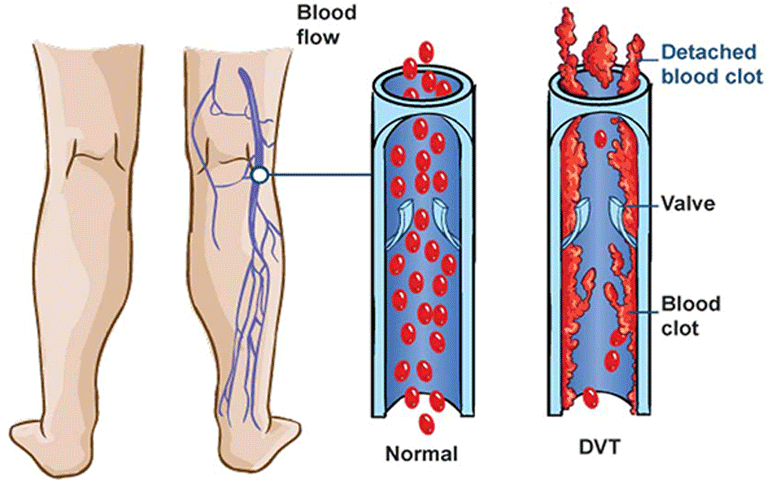
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where blood clots form in deep veins, typically in the legs, leading to pain, swelling, and potential life-threatening complications like pulmonary embolism. Proper DVT management helps protect individuals at risk, including those recovering from surgery, people with limited mobility, and individuals with underlying medical conditions that affect circulation.
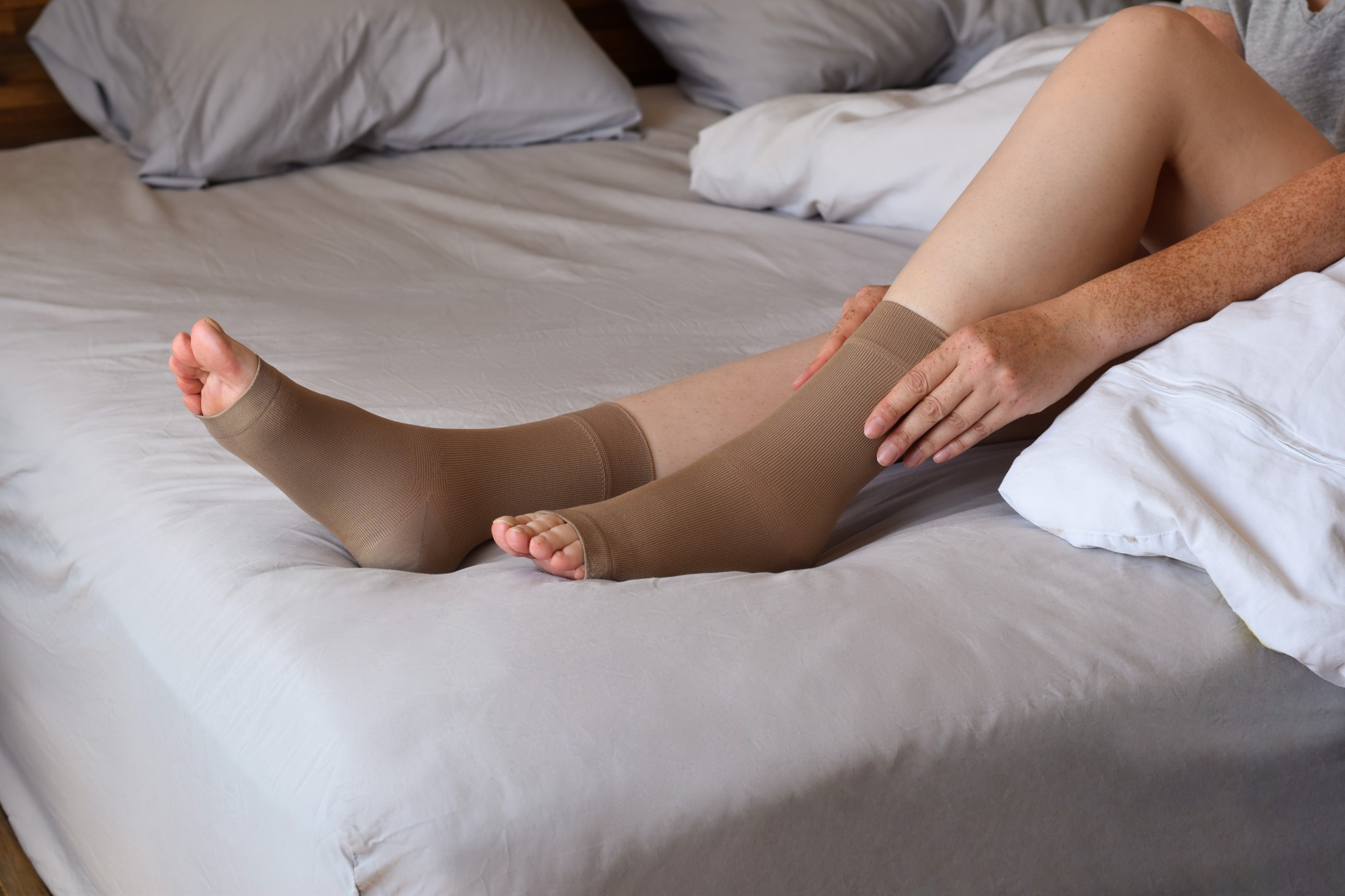
One proven method for DVT management is Intermittent Pneumatic Compression (IPC) therapy. This non-invasive approach uses inflatable cuffs to apply controlled pressure to the legs, mimicking natural muscle contractions and promoting blood flow. By enhancing circulation, IPC helps prevent blood from pooling in the veins, reducing the likelihood of clot formation.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs. These clots develop when blood flow slows down or becomes restricted, often due to prolonged inactivity, injury, or underlying health conditions.
Common Symptoms of DVT
DVT can occur without noticeable symptoms, but when present, they may include:
- Swelling in one leg, often accompanied by a feeling of heaviness
- Pain or tenderness in the calf or thigh, which may worsen with movement
- Red or discolored skin over the affected area
- Warmth around the clot due to inflammation
Since these symptoms can be similar to other conditions, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis.
Potential Complications of DVT
If left untreated, DVT can lead to severe complications, including:
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
If a clot dislodges and travels to the lungs, it can block blood flow, causing shortness of breath, chest pain, and even sudden collapse. PE is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. - Post-Thrombotic Syndrome (PTS)
Some individuals with DVT experience long-term leg pain, swelling, and skin discoloration due to damaged blood vessels, affecting their mobility and quality of life.
Given the serious risks associated with DVT, including complications like pulmonary embolism and post-thrombotic syndrome, managing the condition proactively helps reduce health risks.
Preventive approaches such as Intermittent Pneumatic Compression (IPC) support healthy circulation and lower the chance of clot formation, especially for those recovering from surgery, individuals with limited mobility, or those with a history of vascular conditions.
Who is at Risk for DVT?
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) can affect anyone, but certain individuals are at a significantly higher risk due to lifestyle factors, medical conditions, or genetic predisposition.
DVT management is particularly important for those with restricted mobility, as prolonged inactivity can slow blood circulation, increasing the likelihood of clot formation. Recognizing risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures, such as using Intermittent Pneumatic Compression (IPC) therapy to promote healthy blood flow.
High-Risk Groups for DVT
While deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can affect anyone, certain individuals face a higher likelihood of developing blood clots due to medical conditions, lifestyle factors, or restricted movement.
Individuals Recovering from Surgery
Post-surgical patients, especially after orthopedic, abdominal, or vascular procedures, often experience reduced mobility, increasing their risk of clot formation.
Those with Limited Mobility
People who are bedridden due to illness, paralysis, or extended hospitalization may experience blood pooling in the legs, leading to clot development.
Frequent Travelers
Long flights, car rides, or extended periods of sitting without movement can slow circulation, increasing the risk of travel-related DVT, sometimes called “economy class syndrome.”
People with Clotting Disorders or a Family History of DVT
Genetic conditions such as Factor V Leiden or other clotting disorders make individuals more susceptible to abnormal blood clot formation.
Pregnant Women and Postpartum Individuals
Pregnancy increases pressure on veins in the legs and pelvis, slowing blood return to the heart. Hormonal changes also contribute to an increased risk of clotting, which remains elevated for weeks after childbirth.
Cancer Patients Undergoing Treatment
Certain cancers and treatments, such as chemotherapy, can increase clotting tendencies, making DVT management a critical part of care for oncology patients.
For individuals in these high-risk groups, preventive strategies such as Intermittent Pneumatic Compression (IPC) can help maintain circulation and lower the risk of complications.
How Intermittent Pneumatic Compression (IPC) Supports DVT Management
IPC is a non-invasive therapy that helps improve circulation and lower the risk of blood clot formation. It supports DVT management by encouraging healthy blood flow, making it especially beneficial for individuals at higher risk due to surgery, limited mobility, or underlying medical conditions.
How IPC Works
IPC devices use inflatable cuffs that wrap around the legs, feet, or thighs. These cuffs fill with air in rhythmic cycles, applying gentle pressure to the veins and then releasing it. This process:
- Mimics natural muscle contractions to push blood through the veins, preventing stagnation.
- Enhances venous return, ensuring blood moves efficiently back to the heart.
- Reduces swelling and fluid buildup, particularly after surgery or extended periods of inactivity.
How IPC Helps Prevent Blood Clots
One of the primary concerns with DVT management is preventing blood from pooling in the veins, which increases the risk of clotting. IPC combats this by:
- Stimulating circulation, preventing blood from becoming stagnant in deep veins.
- Reducing vein wall stress, which can contribute to clot formation.
- Aiding in post-surgical recovery, when mobility is often restricted.
IPC vs. Other DVT Prevention Methods
While IPC is an effective tool for DVT management, it is often used in combination with other preventive measures, such as:
- Compression Stockings
- Provide constant, gentle pressure to the legs.
- Improve blood flow but do not offer the same dynamic compression as IPC.
- Anticoagulant Medications (Blood Thinners)
- Help prevent clots but come with risks such as excessive bleeding.
- Not suitable for all patients, especially those with bleeding disorders.
- Physical Movement & Hydration
- Encouraged to keep blood circulating naturally.
- Not always possible for individuals recovering from surgery or those with mobility limitations.
IPC therapy is particularly beneficial for patients who cannot take anticoagulants or need additional support in DVT management.
Benefits of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression for DVT Management
By improving circulation and preventing venous stasis, IPC provides several benefits that support vascular health and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Non-Invasive and Drug-Free Solution
IPC provides a safe, non-pharmaceutical method for DVT management, making it especially useful for individuals who cannot take blood thinners due to medical conditions or a heightened risk of excessive bleeding. Unlike anticoagulant medications, which come with potential side effects and require careful monitoring, IPC offers a mechanical approach to improving circulation.
Enhances Circulation and Reduces Venous Stasis
One of the primary benefits of IPC is its ability to enhance circulation by mimicking the body’s natural muscle contractions. The rhythmic pressure applied by the device encourages blood to flow efficiently back to the heart, preventing it from pooling in the veins. This is particularly useful in reducing venous stasis, a condition where sluggish blood flow increases the risk of clot formation.
Supports Post-Surgical Recovery
Limited mobility after surgery can greatly increase the risk of DVT, as prolonged inactivity slows blood flow and raises the likelihood of clot formation. IPC serves as a passive method of promoting circulation, ensuring that blood continues to move efficiently even when physical movement is restricted. In addition to preventing clots, IPC helps reduce post-operative swelling, which supports faster healing and improves overall comfort during recovery.
Reduces the Risk of Serious Complications
DVT poses significant health risks, and IPC therapy helps lower the chances of life-threatening complications such as pulmonary embolism (PE), where a clot travels to the lungs and blocks blood flow. In addition, IPC therapy reduces the risk of post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS), a chronic condition that can cause long-term pain, swelling, and skin changes due to previous clot formation.
Regular use of IPC not only supports DVT management but also contributes to better long-term vascular health, reducing the likelihood of recurrent clots and improving overall circulation.
When is Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Recommended?
While it is commonly used in hospital or clinical settings, IPC therapy is also beneficial for at-home care, helping to prevent deep vein thrombosis in those who require additional circulatory support.
Post-Surgery Recovery
Patients recovering from orthopedic procedures, such as knee or hip replacements, face a higher risk of DVT due to prolonged immobility. After abdominal or vascular surgeries, blood flow naturally slows, increasing the likelihood of clot formation.
Since movement is often restricted during recovery, Intermittent Pneumatic Compression (IPC) provides a practical solution by stimulating circulation and helping prevent blood from pooling in the veins. For post-operative patients who cannot move around immediately, IPC serves as a reliable method to maintain healthy blood flow and reduce the risk of complications.
Hospitalized Patients with Reduced Mobility
Individuals who are bedridden or recovering in a hospital for extended periods are particularly vulnerable to DVT, as inactivity causes blood to stagnate in the deep veins. Hospitals frequently use IPC devices to prevent hospital-acquired DVT, particularly for patients in intensive care or recovering from major surgeries.
Additionally, trauma and stroke patients who experience limited movement can benefit from passive circulation support through IPC, ensuring blood continues to flow efficiently even when they are unable to move on their own.
At-Home Use for Chronic DVT Prevention
For some individuals, DVT management is a long-term concern due to chronic venous insufficiency or a history of previous clotting episodes. IPC devices designed for home use enable at-risk individuals to continue preventive therapy outside of a hospital setting.
Patients who struggle with walking or standing for extended periods can benefit from consistent IPC therapy to prevent venous stasis, maintaining proper circulation and reducing the likelihood of new clot formation. This makes IPC a valuable option for those who require ongoing clot prevention.
High-Risk Individuals Prone to Blood Clots
As circulation naturally slows with age, older adults face a higher risk of DVT, particularly if they have underlying conditions that affect blood flow. IPC is often recommended for individuals with a history of blood clots, limited mobility due to aging or chronic illness, or medical conditions such as heart disease or obesity that increase clotting risks.
By promoting healthy circulation, IPC therapy helps lower the chance of DVT-related complications and supports long-term vascular health, making it a practical choice for older individuals and those with increased clotting risks.
How to Use IPC Devices for DVT Prevention
When used correctly, these devices provide an effective, non-invasive method for DVT management, particularly for individuals with limited mobility or post-surgical patients. Proper usage is important to ensuring maximum benefits and preventing complications.
How Pneumatic Compression Devices Work
IPC devices consist of inflatable cuffs that wrap around the legs, thighs, or feet. These cuffs are connected to a pump that delivers controlled air pressure in rhythmic cycles. The compression works by:
- Applying gentle pressure to the veins, mimicking the natural pumping action of the muscles.
- Improving venous return, helping blood move efficiently back to the heart.
- Reducing swelling and fluid retention, particularly in post-surgical patients.
How to Wear and Use IPC Devices
To ensure optimal effectiveness, IPC devices should be worn and used according to the manufacturer’s guidelines and healthcare provider’s instructions:
- Position the cuffs correctly – Wrap the cuffs around the calves, thighs, or feet, depending on the prescribed treatment area. The fit should be snug but not too tight.
- Secure the connections – Attach the air tubing from the cuffs to the IPC pump.
- Set the compression cycle – Adjust the device to the recommended settings, which control the pressure intensity and inflation/deflation timing.
- Use the device as prescribed – IPC therapy sessions typically last 20-60 minutes, multiple times per day, or as directed by a healthcare professional.
Consistency for Effective DVT Management
To maximize the benefits of DVT prevention, IPC therapy should be used consistently, particularly for high-risk individuals. Regular use:
- Prevents blood from pooling in deep veins, reducing clot risk.
- Supports post-surgical recovery, helping to prevent complications.
- Enhances circulation over time, promoting overall vascular health.
Consult a Healthcare Provider for Proper Usage
Before beginning IPC therapy, consulting a healthcare provider is important to ensure the treatment is safe and effective. The correct compression settings should be determined based on an individual’s risk factors, medical history, and overall circulation health. A healthcare professional, such as those at Care-Med, can offer expert guidance on determining the appropriate pressure settings and inflation cycles, ensuring optimal effectiveness while minimizing potential risks.
A healthcare provider will recommend the frequency and duration of use needed for optimal results. While some individuals may require short sessions a few times per day, others—such as post-surgical patients or those with chronic circulation issues—may benefit from longer or more frequent IPC therapy. Personalized recommendations ensure that the therapy effectively supports blood flow and prevents clot formation without unnecessary strain on the veins.
It is also important to consider contraindications before using IPC therapy. Certain conditions, such as severe peripheral artery disease (PAD) or untreated deep vein thrombosis, may make compression therapy unsuitable. A medical evaluation can help determine whether IPC is the right approach or if alternative DVT management strategies should be explored.
Supporting Circulation and Preventing DVT with IPC Therapy
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition that requires proactive management to prevent complications such as pulmonary embolism and post-thrombotic syndrome. Intermittent Pneumatic Compression (IPC) offers a non-invasive, effective way to improve circulation and reduce the risk of blood clots—especially for individuals with limited mobility, post-surgical patients, and those at high risk for venous thromboembolism.
By mimicking natural muscle contractions, IPC therapy helps enhance venous return, reduce swelling, and promote overall vascular health. Whether used in hospitals or at home, it provides an essential preventive measure for those unable to take blood thinners or needing additional circulatory support.
If you or a loved one are at risk for DVT, consulting a healthcare professional is the best way to determine the most suitable DVT prevention strategy for your needs. To learn more about compression therapy options, contact Care-Med for expert guidance on IPC devices and benefits. Taking proactive steps today can help support better circulation and long-term vascular health.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Table of Contents
- Intermittent Pneumatic Compression for DVT Management
- What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
- Who is at Risk for DVT?
- How Intermittent Pneumatic Compression (IPC) Supports DVT Management
- Benefits of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression for DVT Management
- When is Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Recommended?
- How to Use IPC Devices for DVT Prevention
- Supporting Circulation and Preventing DVT with IPC Therapy
We specialize in orthotics, body braces, and compression wear tailored to your unique needs in Toronto. Reach out to us at info@caremed.care or call 416-782-5353 to book your fitting and consultation.
Experience the difference of customized solutions designed just for you.